Flavonoids are a group of natural substances found in plant parts including fruits, grains, bark, roots, stems, flowers, etc. They can also be obtained from beverages and wine amongst others. Specific examples include broccoli, grapefruit, pomegranate, soybeans, green tea, skullcap, tomatoes, cherries, apples, etc. They are the most abundant polyphenols in the human diet as they account for about two-thirds of all ingested polyphenols. This flavonoid class has a wide variety of characteristics in higher plants. Many flavonoids are easily recognized as flower pigments in most flowering plants having seeds in fruits. However, their occurrence is not restricted to flowers as they are found in all parts of plants (Dewick, 2002).
These natural products are well known for their beneficial effects on health due to their broad biological activities such as anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, anti-mutagenic, anti-carcinogenic, anti-hepatoprotective, antihypertensive, immune-boosting and antidiabetic activities amidst others, etc.
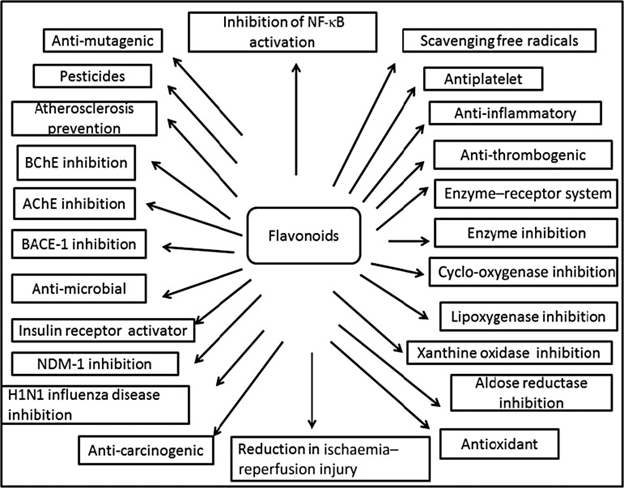
Source: (Panche et al., 2016)
Flavonoids can be classified into flavones (apigenin, luteolin, chrysin, baicalein, baicalin), flavonols (quercetin, kaempferol, myricetin, galangin, fisetin), flavanols (epicatechin gallate, theaflavin, epigallocatechin), anthocyanins (delphindin, cyanidin, malvidin, pelargonidin, peonidin), flavanones (naringenin and hesperetin) and isoflavones (genistein, glycitein, formononetin, daidzein).
Flavonoids subclasses and examples
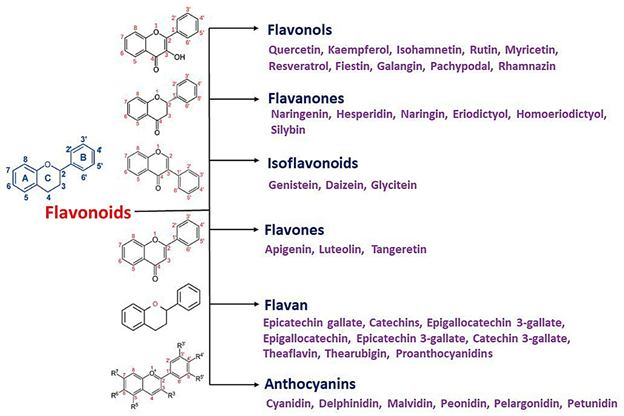
Source: Aboody & Mickymaray (2020)
Flavonols can be found in onions, apples, romaine lettuce, tomatoes, garbanzo beans, turnip greens, sweet potatoes, etc. Flavanols (chalcones) are found in apples, bananas, blueberries, peaches, pears, strawberries, etc. Flavones are found in apples, oranges, watermelon, chili peppers, lettuce, etc. Flavanones are found in oranges, grapefruit, lemons, tomatoes, etc. Anthocyanins are found in blueberries, raspberries, eggplant, black rice, red cabbage, etc. Isoflavonoids are found in soybean, chickpea, lupin seed products, etc.
Flavonoids subclasses and food sources
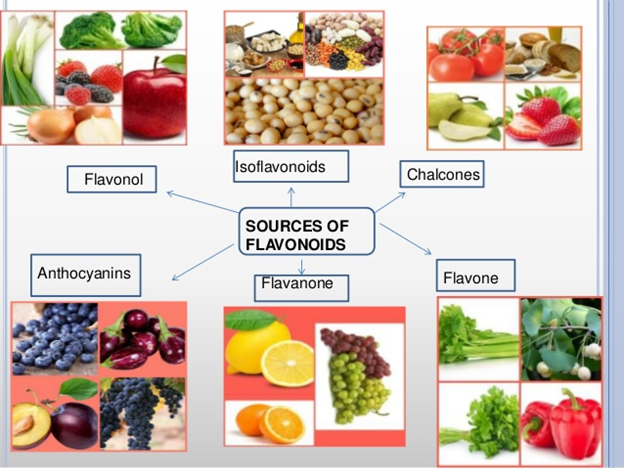
Source: SlideShare.net
References
- Panche, A. N., Diwan, A. D., & Chandra, S. R. (2016). Flavonoids: an overview. Journal of nutritional science, 5.
- Dewick, P. M. (2002). Medicinal natural products: a biosynthetic approach. John Wiley & Sons.
- Aboody, M. S. A., & Mickymaray, S. (2020). Anti-fungal efficacy and mechanisms of flavonoids. Antibiotics, 9(2), 45.
- Cushnie, T. T., & Lamb, A. J. (2005). Antimicrobial activity of flavonoids. International journal of antimicrobial agents, 26(5), 343-356.